Core Web Vitals: What are they and why they are Important?
Table of contents

Google constantly keeps updating its algorithms in an effort to serve its users the best. Hence, the way Google ranks websites keeps changing. Now user experience will play a major role in determining the rank of your website. As you may already be aware of the fact that Google uses over 200 signals to determine the search engine rankings. Most of those metrics mainly focus more on user experience than SEO. Moreover, now Google is introducing a new set of performance metrics to enhance the way it evaluates the entire user experience with already existing signals known as core web vitals.
Announced in 2020, initially, Google said that it would be giving plenty of warning prior to making the update. But in the month of November, Google made a shocking announcement of incorporating Core Web Vitals officially as a ranking signal in May 2021. With such a short time frame, every marketer is struggling to get his website in compliance within time. If you haven’t yet started optimizing your site then you don’t need to worry. Most marketers are still unaware of Core Web Vitals. But ranking factors are always important to take into account because if you fail to follow Google’s signal then you may risk your website’s rank and see your organic traffic suffer. Hence, we at Jacksonville SEO company have come up with this post to help you understand what are Core Web Vitals, why are they important, to help you prepare for this new update.
What are Core Web Vitals?
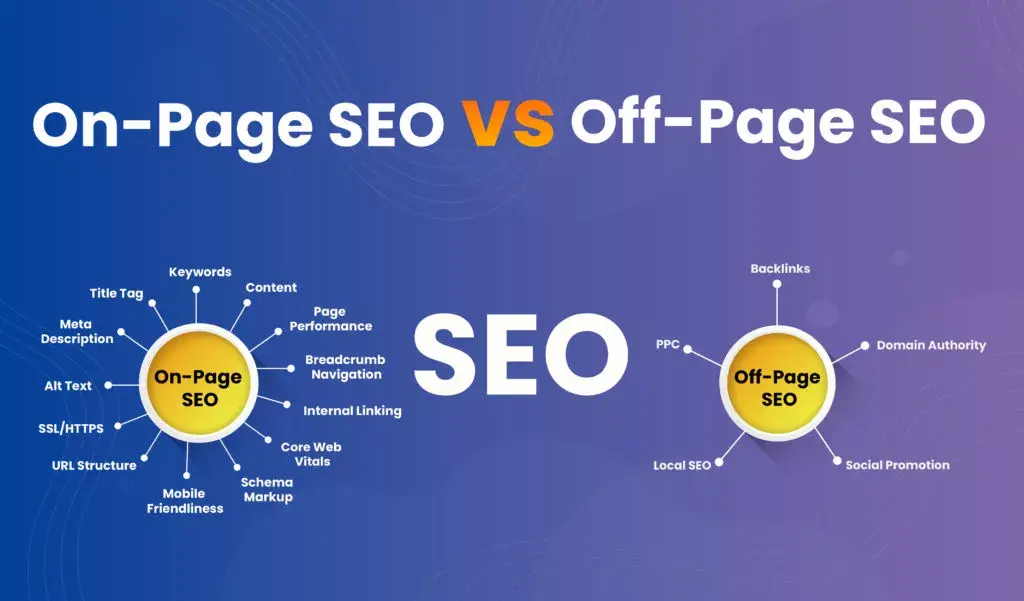
Core Web Vitals are a set of three new metrics that Google considers important to enhance the webpage’s overall user experience. Among those metrics, you have Page Experience signals like mobile optimization, browser safety, usage of HTTPS protocol, and less intrusive pop-up ads that make a page user-friendly. These signals would not have been your priority at the time when you were trying to reach the top of search engines before. Rather you would have been worried more about keyword optimization, metadata, content, etc. But now Google will also consider the website’s performance while determining the search results with the Web Vitals initiative. Thus generating the need to enhance your website’s user experience. The aim is to figure out the page experience signals that have the most significant impact on user experience.
The metrics that we have been talking about so far are Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), and First Input Delay (FID) designed to measure loading, visual stability, and interactivity respectively. You can easily measure these metrics and if you fall within a specific threshold, you will get a boost in your ranking. Or else, you can optimize your website accordingly to get benefited from this update. So, let us go over those three Core Web Vitals and know what they are.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
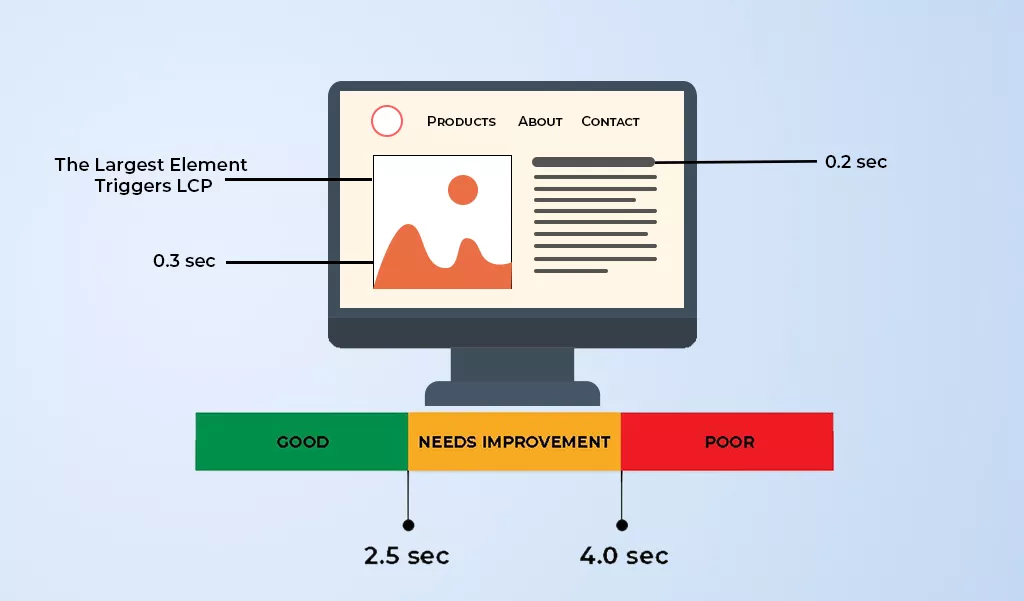
The Largest Contentful Paint usually measures the loading performance. In other words, it is the time taken by a page to load from the point of view of an actual user. It is different from other measurements used to measure page speed. When we usually measure the website’s loading speed, we talk about numbers such as the loading speed is 2 seconds or 3 seconds. But this is not the most accurate way to measure your website’s speed. Because, you might have seen that when you visit a website, it does not load in a shot. Some elements of the website might appear to load before others.
For example, let us consider that you visit a website with a logo, a video, few images, and content. While the content, logo, and some images will load faster, you will see that the video might take time.
The user tends to leave the site if it takes longer than three seconds to load. This is why Google uses LCP as one of its Core Web Vitals. LCP or Largest Contentful Paint measures the time taken for the largest element on the page to load and determines how long it takes for a page to finish loading. As soon as this update will roll out, Google will start measuring the websites it ranks for these elements. So, it is crucial to keep LCP times under the threshold.
So, to improve your site’s LCP you should take the following points into consideration:
- Remove the unnecessary third-party scripts as they can slow down the page by 34 ms.
- Upgrade to a better web host to boost your loading speed.
- If one of the large elements is slowing down your page speed and is not so important, remove it.
- Minimize your CSS as bulky CSS can delay LCP times.
You can also consider other effective ways to speed up your website.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
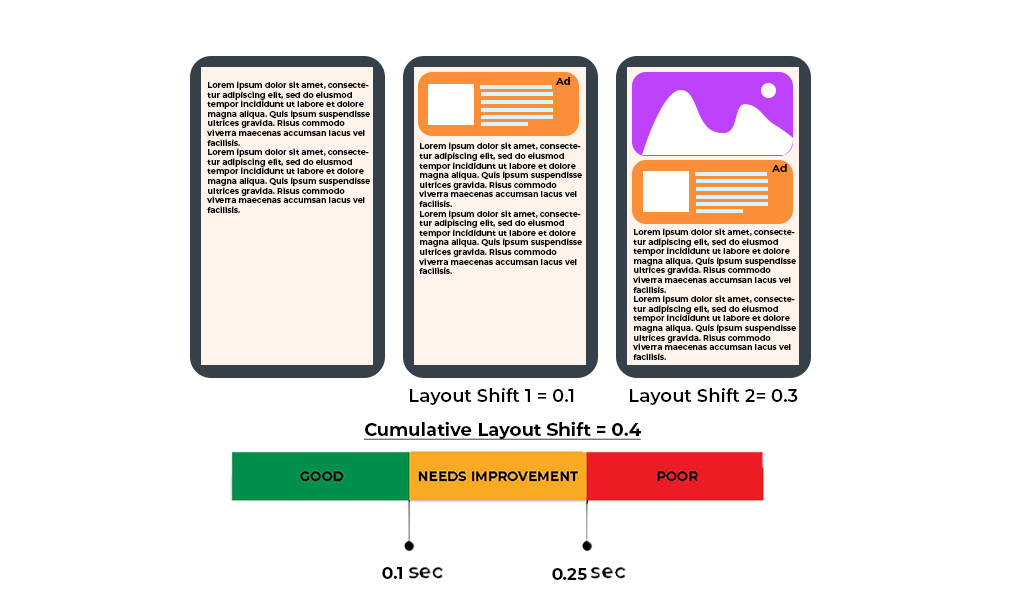
Cumulative Layout Shift measures visual stability that means how elements move around or how stable is the pay layout. In other words, this metric tries to determine the rate of stability of stuff that loads onto your screen. You, sometimes, may have visited a website where button loads inviting you to click on it. But there is still a large content being loaded in the background. As a result, when you try to hit that button, it gets pushed down a bit just at that moment when the content fully loads. Quite annoying, right? Hence, the elements of your page like fonts, text, images, or buttons move around unexpectedly then this is flagged as a terrible user experience.
This shift can also happen due to ads. Though ads being a lifeline of many websites, many of them often tend to load slowly which can frustrate the user. Additionally, the biggest contributors to a poor Cumulative Layout Shift are images, embeds, and iframes without dimensions, content injected with JavaScript, and fonts and styles applied late in the load.
To determine the movement of elements, the Cumulative Layout Shift metric usually compares the frames. It calculates the severity of those moments by taking all the points at which layout shift happens. So, in order to clear this checkpoint, the CLS of your page should be less than 0.1 FYI. To be deemed good make sure to have as low CLS as possible.
You can consider some simple things to avoid all unexpected layout shifts or to minimize your CLS:
- Make sure to include size attributes to your images and videos. Alternatively, you can also use CSS aspect ratio boxes to reserve the required space. This will help the browser to allocate the right amount of space while the image is loading in the document. Hence, they won’t appear suddenly on the page pushing the content down.
- Avoid inserting content above existing content except in response to user interaction.
- Add new elements below the fold so that they don’t push the content down or to the side.
Prefer to transform animations if you are using CSS to animate elements.
First Input Delay (FID)
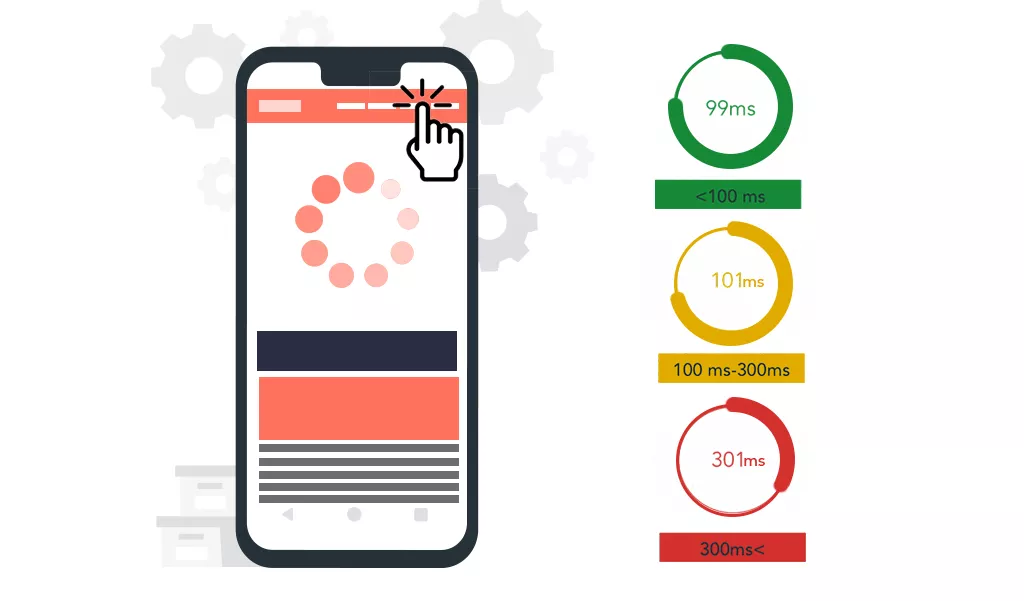
Now let us take a look at Google’s third Core Web Vital, the First Input Delay. This metric measures the time it takes for a user to actually interact with your page. Elaborating it, we can say that it measures the time from when a user first interacts with a page to the time when the browser actually starts processing event handlers in response to that interaction. According to Google, this event should take place within 100 milliseconds after the user arrives on the page. While the FID between 100 to 300 ms needs improvement and if it is above 300 ms then it is considered poor.
Google considers the First Input Delay metric as the most important metric because it is purely user-centric. It is all about the experience of the user that visits your website and requires user interaction in order to measure it.
In simple terms, FID measures interactivity. These interactions include selecting an option from a menu, clicking on a link, and entering the email into a field. While scrolling or zooming is not included in them.
When a browser is busy and thus unable to process an action from a user, input delay or input latency occurs. This typically happens when a page has a large amount of JavaScript code that needs to be executed. So, in order to improve your FID take a look at the following points.
- Break the long tasks into smaller and asynchronous tasks because long tasks do not allow the main thread to process user input by blocking it. Breaking them into smaller tasks will help user input to be processed between them. Make sure that your tasks are under 50 ms.
- Minimize the amount of data that needs to be post-processed on the client side. This will help to reduce the amount of work that needs to be done by the browser to render a page.
- Use web workers to reduce the workload on the main thread. They will allow you to delegate some of the JavaScript code to run on a worker thread.
- Make use of async or defer so that JavaScript executes only when needed. In case you use modern JavaScript, configure ES6 modules to load on demand.
- Remove non-critical third-party scripts as they can negatively impact FID.
- Use a browser cache that will help load the content on your page faster.
Now as you have understood about the Core Web Vitals, let us know their importance in detail.
Why are Core Web Vitals Important?
Google always prioritizes its users and aims to provide them the best experience so Core Web Vitals will now directly influence your rankings. If your website compiles with them, it is likely to rank higher. Otherwise, you will end up losing your website’s rank. So, it will be appropriate to say that poorly designed websites will not cut it with no focus on user experience.
Page experience will be a mix of factors like website security, mobile-friendliness, lack of interstitial pop-ups, and safe browsing. These are considered important for user experience for Google and Core Web Vitals will be a supper essential part of that score. In fact, they will make up the biggest chunk of your page experience score.
Moreover, by optimizing your site for this new update, your website will be eligible for Google top stories on mobile. Ultimately gaining you a huge amount of traffic as most of the traffic comes from mobile devices. But remember that page experience should go hand in hand with high-quality and relevant content. Because both these factors give you an upper hand over your competitors.
The bottom line is you eventually boost your website’s rank, visibility, traffic and thus enhance your revenue by providing the best user experience. So, now you must have clearly understood why focusing on your site’s vitals is necessary. Here are some of the reasons how web design affects your business?
Conclusively, we can say that if you follow all the best practices of using popups then you can definitely overweigh the rewards over the risks. A popup ad that doesn’t look intrusive and nagging is well appreciated by the people. Moreover, well-timed popups with relevant messages targeting the right audience can provide all the above-mentioned benefits. So, we would always suggest considering the usage of popups on your website but the final decision is yours.
If you want to get an idea about what are the things present in the top-ranking that make them successful, and that you can implement for your website here is an article on 10 things successful websites have in common
We hope that this article must have helped you in understanding all the benefits and shortcomings of using popups on your website and now you can make your sensible decision on whether to use them on your website or not. If you need any advice on, how can you effectively use the popups in your website, you can contact a website design company and begin achieving your goals.